本文是对 iOS 中 GCD (Grand Central Dispatch) 的整理小结。总结了有关线程的知识点、GCD 的对应的使用方法。
线程与进程 线程是系统能够进行运算调度的最小单位,线程被包含在进程中,是进程中的实际运作单位。一个程序至少有一个进程,一个进程至少有一个线程。一个进程中可以并发多个线程,执行不同的任务,可充分利用系统资源,提高性能。
进程是系统进行资源分配和调度的一个独立单位。线程自己基本上不拥有系统资源,同一个进程中的多个线程共享进程所拥有的资源。当多个线程对同一个资源进行操作的时候需要注意线程安全问题。
iOS 中的程序启动,创建好一个进程的同时, 一个线程便开始运行,这个线程叫主线程。有关界面的显示操作,即 UIKit 的操作在主线程进行。 有关多线程的操作,主要依靠 GCD 和 NSOperation。
相关概念
串行(Serial):在固定时间内只能执行单个任务。
并行(Parallel):在固定时间内同时执行多个任务。
并发(Concurrent):在固定时间内可以执行多个任务。它和并行(Parallel)的区别在于,并发不会同时执行多个任务,而是通过在任务间不断切换去完成多个任务,多个任务在同一时间间隔内执行。
同步(Sync):会把当前的任务加入到队列中,除非该任务执行完成,线程才会返回继续运行,也就是说同步会阻塞线程。任务在执行和结束一定遵循先后顺序,即先执行的任务一定先结束。
异步(Async):会把当前的任务加入到队列中,但它会立刻返回,无需等任务执行完成,也就是说异步不会阻塞线程。任务在执行和结束不遵循先后顺序。可能先执行的任务先结束,也可能后执行的任务先结束。
串行是同步的执行方式。
GCD 简介 GCD (Grand Central Dispatch) 是一个异步执行的技术,将应用程序中线程管理的代码在系统层级中实现,开发者只要定义想执行的任务并追加到适当的 Dispatch Queue 中,GCD 就能生成必要的线程执行任务,就是用非常简洁的方法,实现了复杂繁琐的多线程编程。
1 2 3 dispatch_async(queue, ^{ //执行任务 });
使用 Block 语法定义要执行的任务,通过 dispatch_async 函数将任务追加到 queue 队列中,这样就可以使指定的 Block 在另一线程中执行。
1、Dispatch Queue 两种队列:串行队列 Serial Dispatch Queue;并发队列 Concurrent Dispatch Queue。
1.1 创建队列的方法: 1、dispatch_queue_create 函数
1 2 3 // 串行队列 DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL,可写成 NULL // 并发队列 DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create("com.my.queue", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL);
第一个参数指定队列的名称,方便调试。
第二个参数 Serial Dispatch Queue 指定为 NULL,Concurrent Dispatch Queue 指定为 DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT。
返回值为 Dispatch Queue,dispatch_queue_t 类型
2、获取系统标准提供的 Dispatch Queue
1 2 dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0); dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_main_queue();
Main Dispatch Queue 是在主线程执行的队列 ,主线程只有1个,所以 Main Dispatch Queue 是串行队列 Serial Dispatch Queue。有关用户界面更新等一些必须在主线程中执行的处理,需要追加到 Main Dispatch Queue 中处理。这与 performSelectorOnMainThread 执行方法相同。
Global Dispatch Queue 是所有应用程序都能使用的 Concurrent Dispatch Queue,没有必要通过 dispatch_queue_create 生成,只要获取 Global Dispatch Queue 使用即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 //Global Dispatch Queue 有4个执行优先级,向队列中追加处理时,应选择与处理内容对应的优先级。 #define DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_HIGH 2 //高优先级 #define DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT 0 //默认优先级 #define DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_LOW (-2) //低优先级 #define DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND INT16_MIN //后台优先级
1.2 串行队列 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create("com.my.queue", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"1 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"2 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"3 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"end"); //end //1 --- <NSThread: 0x600003fded40>{number = 8, name = (null)} //2 --- <NSThread: 0x600003fded40>{number = 8, name = (null)} //3 --- <NSThread: 0x600003fded40>{number = 8, name = (null)}
串行队列,要等待当前任务处理结束,1执行结束,接着执行2,如此重复,同时执行的处理数只能有一个,顺序执行任务。
1.3 并发队列 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create("com.my.queue", DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"1 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"2 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"3 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"end"); //end //2 --- <NSThread: 0x600003fded40>{number = 4, name = (null)} //3 --- <NSThread: 0x600003fded40>{number = 6, name = (null)} //1 --- <NSThread: 0x600003fded40>{number = 8, name = (null)}
并发队列,使用多个线程同时执行多个处理,不用等待当前任务处理结束,就开始执行后面的任务,可并发执行多个任务,得到的结果打印顺序,不会按照代码追加到队列的顺序,是打乱的。
2、dispatch_sync 同步操作函数、dispatch_async 异步操作函数
2.1 在串行队列上进行同步/异步操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create("com.my.serial1", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL); dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"1 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"11 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"2 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"22 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"3 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"33 --- "); //1 --- <NSThread: 0x600002662200>{number = 1, name = main} //11 --- <NSThread: 0x600002662200>{number = 1, name = main} //2 --- <NSThread: 0x600002662200>{number = 1, name = main} //22 --- <NSThread: 0x600002662200>{number = 1, name = main} //3 --- <NSThread: 0x600002662200>{number = 1, name = main} //33 ---
在串行队列上进行同步操作,所有任务将顺序执行。不会开启线程,在主线程上顺序执行任务,相当于直接执行任务的代码。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create("com.my.serial2", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"a --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { sum += 1; } NSLog(@"--- %d", sum); }); NSLog(@"aa --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"b --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"bb --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"c --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"cc ---"); //aa --- <NSThread: 0x600002662200>{number = 1, name = main} //a --- <NSThread: 0x6000026d3000>{number = 8, name = (null)} //bb --- <NSThread: 0x600002662200>{number = 1, name = main} //cc --- //--- 100000 //b --- <NSThread: 0x6000026d3000>{number = 8, name = (null)} //c --- <NSThread: 0x6000026d3000>{number = 8, name = (null)}
在串行队列上进行异步操作,如上代码,打印顺序不固定,但是 aa – bb – cc 一定是按照这个顺序打印的。a – b – c – 一定是按照这个顺序处理队列的任务的,异步执行另开一个线程,执行串行队列里的任务,一次只能执行一个任务,a 执行完,再执行 b,以此类推。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create("com.my.serial3", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL); NSLog(@"1 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"2 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"3 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"4 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"5 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); //1 --- <NSThread: 0x6000010d21c0>{number = 1, name = main} //2 --- <NSThread: 0x6000010d21c0>{number = 1, name = main} //4 --- <NSThread: 0x6000010d21c0>{number = 1, name = main} //5 --- <NSThread: 0x6000010d21c0>{number = 1, name = main} //3 --- <NSThread: 0x600001086880>{number = 4, name = (null)}
在串行队列上进行,同步、异步嵌套。串行队列一次只能执行一个任务,同步执行的函数要等待 block 任务执行完成后,再去执行嵌套的串行队列上的 block 任务,所以打印的顺序为 1 – 2– 4 – 3,5的顺序不固定,可能在 3 前,可能在 3 后。一定是 1 – 2 – 4 先执行完,然后串行队列才能让 3 执行,一个任务执行完,才能执行下一个任务。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create("com.my.serial5", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL); NSLog(@"1 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"2 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"3 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"4 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"5 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); //1 --- <NSThread: 0x600001ea6280>{number = 1, name = main} //2 --- <NSThread: 0x600001efc6c0>{number = 4, name = (null)} //5 --- <NSThread: 0x600001ea6280>{number = 1, name = main} //崩溃,死锁
在串行队列上进行,异步、同步嵌套。如上代码,会产生死锁。
同样的在串行队列上,同步嵌套,也会产生死锁。这就是我们常常遇到的主线程死锁问题。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create("com.my.serial5", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL); dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ //... }); }); //上面的代码,在第二个 dispatch_sync 执行时就会发生死锁 //当前串行队列有任务正在执行,相互等待,死锁 //在项目中经常遇到,切换到主线程执行的情况这时需要注意了 - (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; dispatch_sync(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{ //主线程死锁 }); } //第三方库 SDWebImage 提供一种解决方法 dispatch_main_async_safe(block) if (dispatch_queue_get_label(DISPATCH_CURRENT_QUEUE_LABEL) == dispatch_queue_get_label(dispatch_get_main_queue())) { block(); } else { dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), block); } //先判断当前任是否在主队列上,如果是直接执行任务就行了,不用切换到主队列上 //否则的话用异步调用主队列,执行任务。这样可避免主线程死锁
谨慎使用同步操作。其实在主线程队列中使用同步操作是一定会构成死锁的,所以建议在串行队列中不要使用同步操作。
2.2 在并发队列上进行同步/异步操作 与上面串行队列操作类似:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_HIGH, 0); dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"1 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"11 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"2 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"22 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"3 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"33 --- "); //1 --- <NSThread: 0x6000021d1cc0>{number = 1, name = main} //11 --- <NSThread: 0x6000021d1cc0>{number = 1, name = main} //2 --- <NSThread: 0x6000021d1cc0>{number = 1, name = main} //22 --- <NSThread: 0x6000021d1cc0>{number = 1, name = main} //3 --- <NSThread: 0x6000021d1cc0>{number = 1, name = main} //33 ---
在并发队列上进行同步操作,所有任务顺序执行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_HIGH, 0); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"a --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { sum += 1; } NSLog(@"a --- %d %@", sum,[NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"aa --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"b --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { sum += 1; } NSLog(@"b --- %d %@", sum,[NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"bb --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"c --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { sum += 1; } NSLog(@"c --- %d %@", sum,[NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"cc ---"); //aa --- <NSThread: 0x600003a1e380>{number = 1, name = main} //a --- <NSThread: 0x600003a7c440>{number = 5, name = (null)} //bb --- <NSThread: 0x600003a1e380>{number = 1, name = main} //b --- <NSThread: 0x600003a16ac0>{number = 3, name = (null)} //cc --- //c --- <NSThread: 0x600003a85240>{number = 7, name = (null)} //a --- 100000 <NSThread: 0x600003a7c440>{number = 5, name = (null)} //b --- 100000 <NSThread: 0x600003a16ac0>{number = 3, name = (null)} //c --- 100000 <NSThread: 0x600003a85240>{number = 7, name = (null)}
在并发队列上进行异步操作,另开线程各自执行,如上打印情况,只能确定 aa – bb – cc 这样的执行顺序,block 内的打印顺序不确定,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_HIGH, 0); NSLog(@"1 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"2 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"3 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { sum += 1; } NSLog(@"3 --- %d %@", sum, [NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"4 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"5 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); //1 --- <NSThread: 0x60000038e200>{number = 1, name = main} //2 --- <NSThread: 0x60000038e200>{number = 1, name = main} //4 --- <NSThread: 0x60000038e200>{number = 1, name = main} //3 --- <NSThread: 0x6000003d6a80>{number = 6, name = (null)} //5 --- <NSThread: 0x60000038e200>{number = 1, name = main} //3 --- 100000 <NSThread: 0x6000003d6a80>{number = 6, name = (null)}
在并发队列中进行同步、异步嵌套,不会构成死锁。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_HIGH, 0); NSLog(@"1 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"2 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); dispatch_sync(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"3 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"4 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"5 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); //1 --- <NSThread: 0x60000038e200>{number = 1, name = main} //5 --- <NSThread: 0x60000038e200>{number = 1, name = main} //2 --- <NSThread: 0x6000003dc580>{number = 4, name = (null)} //3 --- <NSThread: 0x6000003dc580>{number = 4, name = (null)} //4 --- <NSThread: 0x6000003dc580>{number = 4, name = (null)}
在并发队列中进行异步、同步步嵌套,并发队列,可多任务并发处理,不会构成死锁。
3、dispatch_barrier_async、dispatch_barrier_sync 栅栏函数,像一个分界线,将同一个队列中的任务分开。分隔开的任务,前半部分任务执行完,栅栏函数执行,栅栏函数执行完,后半部分再执行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create("my.queue", DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"%@ --1 ",[NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"%@ --2 ",[NSThread currentThread]); }); //等待栅栏函数执行完,再执行后面的任务 dispatch_barrier_async(queue, ^{ [NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:2]; NSLog(@"%@ -- 分隔线 ",[NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"%@ --3 ",[NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ NSLog(@"%@ --4 ",[NSThread currentThread]); }); NSLog(@"-- end"); // -- end // <NSThread: 0x6000024d4280>{number = 4, name = (null)} --1 // <NSThread: 0x6000024a7bc0>{number = 6, name = (null)} --2 // <NSThread: 0x6000024a7bc0>{number = 6, name = (null)} -- 分隔线 // <NSThread: 0x6000024a7bc0>{number = 6, name = (null)} --3 // <NSThread: 0x6000024d4280>{number = 4, name = (null)} --4
注意,上面使用的自定义的队列 dispatch_queue_create(),如果使用 dispatch_get_global_queue() 队列则栅栏没有分割效果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 //如果将上面的代码,栅栏函数换成 dispatch_barrier_sync 同步的,打印内容如下 //注意 end 打印位置,主线程被阻塞,等待 dispatch_barrier_sync 任务执行完成返回,然后才继续下面的任务 // <NSThread: 0x6000010cb480>{number = 4, name = (null)} --2 // <NSThread: 0x6000010ed540>{number = 6, name = (null)} --1 // <NSThread: 0x600001088f00>{number = 1, name = main} -- 分隔线 // -- end // <NSThread: 0x6000010ed540>{number = 6, name = (null)} --3 // <NSThread: 0x6000010cb480>{number = 4, name = (null)} --4
4、dispatch_after 在指定时间后处理任务,可以使用 dispatch_after 函数来实现
1 2 3 4 dispatch_after(dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, (int64_t)(3 * NSEC_PER_SEC)), dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{ NSLog(@"done ---"); });
dispatch_after 函数不是在指定时间后执行处理,而是在指定时间追加处理到 Dispatch Queue 中。上面例子,与在3秒后用 dispatch_async 函数追加 block 任务到 Main Dispatch Queue 的操作相同。
5、Dispatch Group 在多线程中想监控,追加到队列中的任务都全部完成后,然后再进行处理,这种情况可以使用 Dispatch Group。例如处理完页面所有数据后,最后再在主线程上刷新页面。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0); dispatch_group_t group = dispatch_group_create(); dispatch_group_async(group, queue, ^{ NSLog(@"1 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_group_async(group, queue, ^{ NSLog(@"2 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_group_async(group, queue, ^{ NSLog(@"3 --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_group_notify(group, dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{ NSLog(@"done --- %@", [NSThread currentThread]); }); //2 --- <NSThread: 0x600001969c80>{number = 12, name = (null)} //3 --- <NSThread: 0x6000019fd800>{number = 10, name = (null)} //1 --- <NSThread: 0x600001983500>{number = 11, name = (null)} //done --- <NSThread: 0x600000fae280>{number = 1, name = main}
dispatch_group_wait 函数,在指定的时间内,等待追加到 group 的 队列中的任务是否执行完毕。
1 2 3 4 5 dispatch_time_t time = dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, 3 * NSEC_PER_SEC); long result = dispatch_group_wait(group, time); if (result == 0) { //追加到 group 的 队列中的任务全部执行完毕 }
6、dispatch_apply dispatch_apply 函数按指定的次数将指定的 block 追加到指定的 Dispatch Queue 中,并等待全部处理执行结束。
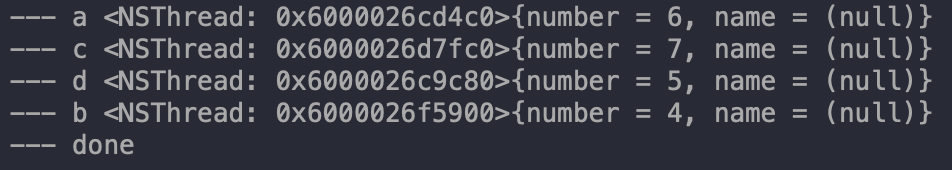
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 NSArray *array = @[@"a", @"b", @"c", @"d"]; dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0); dispatch_async(queue, ^{ dispatch_apply(array.count, queue, ^(size_t index) { NSLog(@"--- %@ %@", array[index], [NSThread currentThread]); }); dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{ NSLog(@"--- done"); }); });
7、Dispatch Semaphore Dispatch Semaphore 是持有计数的信号。
dispatch_semaphore_create 函数可以生成信号量,参数是信号量计数的初始值。
dispatch_semaphore_wait 函数,当信号量值为 0 时等待,等待直到超时,参数可设置超时时长。信号量值大于等于 1 时,不等待,同时将信号量值减 1。
dispatch_semaphore_signal 函数会让信号量值加 1,如果有通过dispatch_semaphore_wait 函数等待信号量值增加的线程,会由系统唤醒最先等待的线程执行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0); dispatch_semaphore_t semaphore = dispatch_semaphore_create(1); NSMutableArray *array = [NSMutableArray array]; for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { dispatch_async(queue, ^{ dispatch_semaphore_wait(semaphore, DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER); [array addObject:[NSNumber numberWithInt:i]]; dispatch_semaphore_signal(semaphore); }); }
在 iOS 开发时,经常遇到一个页面有多个网络数据请求的场景,等多个网络请求获取到数据后再去刷新页面,那么这是就可以使用 Dispatch Semaphore 可与 Dispatch Group
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 NSMutableArray *images = [NSMutableArray array]; dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0); dispatch_group_t group = dispatch_group_create(); dispatch_group_async(group, queue, ^{ dispatch_semaphore_t semaphore1 = dispatch_semaphore_create(1); dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0), ^{ //开始下载第一张图片 NSData *imageData = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:[NSURL URLWithString:@"https://xxxx.png"]]; NSString *path=[NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory,NSUserDomainMask,YES) objectAtIndex:0]; NSString *filename=[path stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"banner1.png"]; //在该路径下创建图片文件,并将存储图片的数据存到本地 NSFileManager* fm = [NSFileManager defaultManager]; [fm createFileAtPath:filename contents:imageData attributes:nil]; [images addObject:filename]; dispatch_semaphore_signal(semaphore1); }); dispatch_semaphore_wait(semaphore1, DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER); }); dispatch_group_async(group, queue, ^{ dispatch_semaphore_t semaphore2 = dispatch_semaphore_create(0); dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0), ^{ //开始下载第二张图片 NSData *imageData = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:[NSURL URLWithString:@"https://xxxx.png"]]; NSString *path=[NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory,NSUserDomainMask,YES) objectAtIndex:0]; NSString *filename=[path stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"banner2.png"]; NSFileManager* fm = [NSFileManager defaultManager]; [fm createFileAtPath:filename contents:imageData attributes:nil]; [images addObject:filename]; dispatch_semaphore_signal(semaphore2); }); //初始化信号量计数为0,会一直等待下载图片 //上面的异步下载图片完成后会调用 dispatch_semaphore_signal 函数 // 然后信号量计数加 1,这时不在等待,该任务执行完成返回 dispatch_semaphore_wait(semaphore2, DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER); }); dispatch_group_notify(group, queue, ^{ //当监控得到追加队列里的任务都完成后,调用本 block 任务 dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{ //当获取全部数据后,在主线程进行刷新页面 NSString *image1 = [images firstObject]; if (image1 && [image1 isKindOfClass:[NSString class]]) { self.imageView1.image = [[UIImage alloc] initWithContentsOfFile:image1];; } NSString *image2 = [images lastObject]; if (image2 && [image2 isKindOfClass:[NSString class]]) { self.imageView2.image = [[UIImage alloc] initWithContentsOfFile:image2];; } }); });
8、dispatch_once dispatch_once 函数时保证在应用程序执行中只执行一次指定处理的 API。
1 2 3 4 static dispatch_once_t onceToken; dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{ // code to be executed once });
Reference 底层并发 API iOS 如何高效的使用多线程 深入浅出 iOS 并发编程